Many water plants today still apply traditional processes to treat groundwater or surface water for domestic use. Besides clean water, a large volume of sludge solution is a concern. Traditional methods such as mud drying yards are time-consuming, polluting the environment, and not workable for large-scale factories.
Sludge dewatering machines have also been put into use, but are mostly old and outdated (such as plate presses, belt presses). Frequent blockages and breakdowns disrupt the operation of the whole plant. It is not suitable for the production expansion plan to meet the increasing demand for clean water for the people. That's when the decanter centrifuge has martial arts.

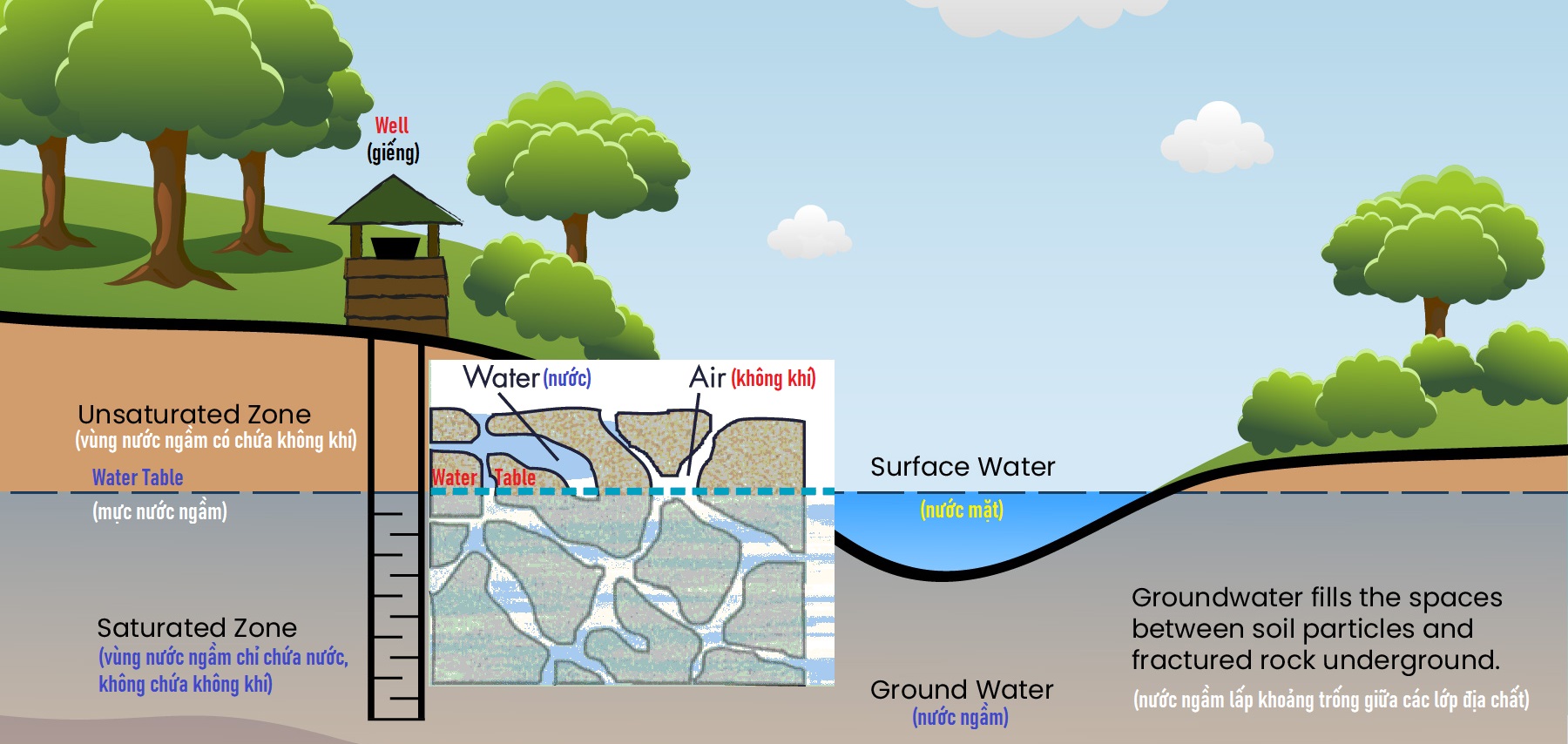
What is water supply? What is groundwater?
Water supply is mainly groundwater that is treated at water plants, before being supplied to residential areas through underground water pipes, serving the basic needs and daily activities of people.
The initial advantage of groundwater is low turbidity because of its permeation through many geological layers. If flowing through deep layers of soil containing sand and granite will dissolve some minerals. If it penetrates through the limestone layers, it will have a high hardness. Microorganisms are rarely found in water because groundwater is located deep in the ground. Their growth is restricted in anaerobic environments.
Feed water contains many types of dissolved minerals such as iron, magnesium, manganese, calcium, etc. These metals will accumulate over time, causing great harm to human health and damage and corrosion of storage systems. Therefore, a prerequisite of a feedwater treatment system is to remove or reduce these components. Water will be treated physicochemically, solids will be removed as sludge.
The pH of groundwater is usually between 4 – 4.5, slightly acidic. The initial groundwater pumped up is usually very clear. But after exposure to air, it will turn yellow-brown because of oxidation of iron in water:
4 Fe2+ (aq) + O2 (g) + 4 H+ (aq) → 4 Fe3+ (aq) + 2 H2O (l)
Fe3+ (aq) + 3 H2O (l) → Fe(OH)3 (s) + 3 H+ (aq)
Treatment of feed water with the input source being river water
Determining the characteristics of the input water source is the first thing to do. Indicators of water quality and specific characteristics of the river must be analyzed.
River water is surface water, so it will have high turbidity and contain many suspended substances (alluvium), dissolved metals, and microorganisms. Pollution levels of surface water sources often change depending on the season. As well as the geology of the riverbed and the tributaries through which the river flows.
In particular, the water used by rivers, and lakes must not be contaminated with salt. Otherwise, it will damage the equipment and tanks in the entire system. Desalination treatment requires a more modern, well-invested, specialized system.
The input surface water sample, as well as the finished product supply water, needs to be appraised and evaluated by the analysis centers. Salinity, pH, dissolved solids content, Ammonium, Arsenic, microbial indicators, manganese, and iron, ... are mandatory criteria to measure. They determine which feed water treatment technology is applied.
Note:
→ Do not use river sections near sewage systems of industrial parks, factories, and residential areas. Because these areas are often heavily contaminated. Especially heavy metals and toxic organic substances.
Water treatment technology is selected according to the following criteria:
- Ensure the stable and standard operation of the system
- The most economical cost of installation, operation, and maintenance.
- There are backup tanks that can be used for 1-2 days. Prevent incidents, and ensure continuous water supply.
- There are sewage and sludge storage tanks. Can be stored for at least 1 day in case sludge treatment fails.

SUPPLY WATER TREATMENT PROCESS
This article will give an example of a common feed water treatment process:
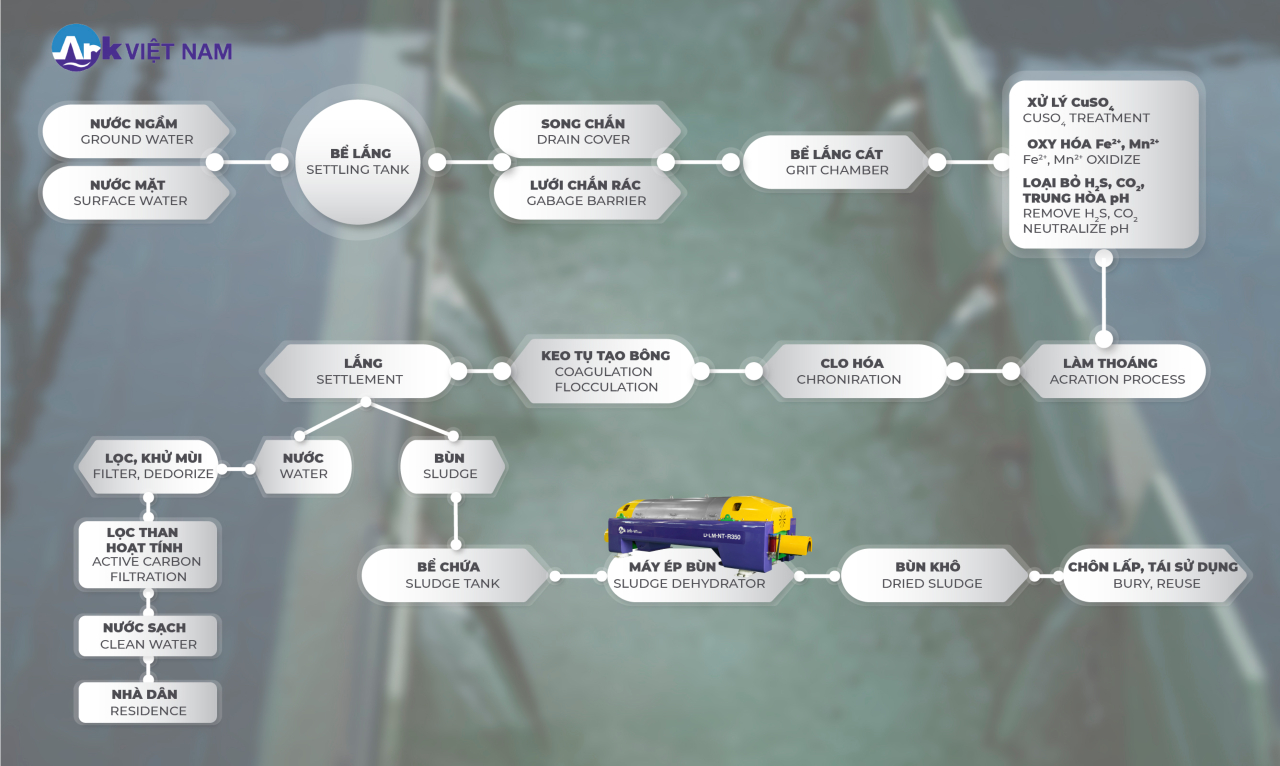
1. Primary treatment
- The input water will be taken through the settling tank to remove suspended sediment. Perform natural oxidation reactions to kill bacteria.
- After that, the inlet water will flow through the screens and screens. Solid waste, garbage, and suspended objects the size of a toothpick or more will be removed.
2. Sand settling tank
The sand settling tank is the next stage. If the water has high turbidity (≥ 250 mg/l) then suspended particles with a size ≥ 0.2 mm and a density ≥ 2.6 – will be removed here. Because they will wear down the movement of the machinery and destroy the reactions in the flocculation tank and the subsequent settling tank.
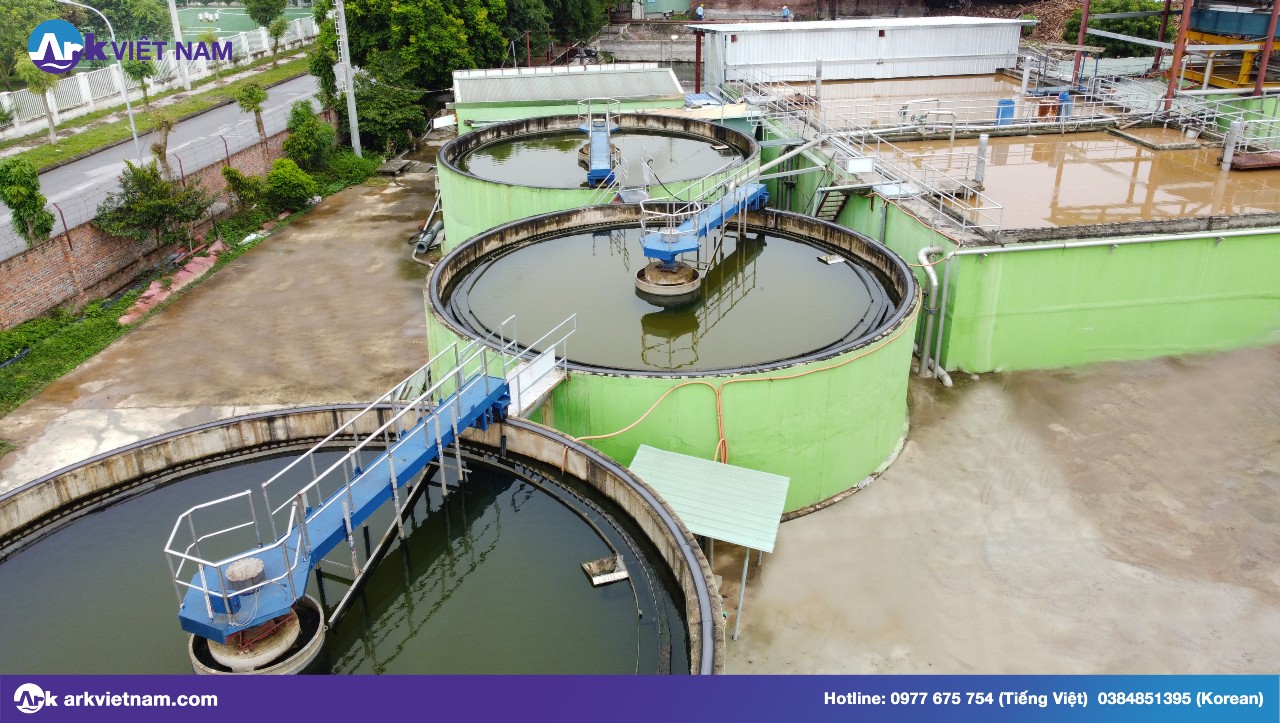

3. Chemical treatment, aeration
At the chemical stage, the water will be treated with chemicals to kill microorganisms, and algae and remove odors. The chemical is usually CuSO4, the dose depends on the concentration of microorganisms, algae, alkalinity, and temperature of the water.
Next is the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+; Mn2+ becomes Mn3+, Mn4+ forms Fe(OH)3, and Mn(OH)2 compounds that precipitate and are removed. Remove gases such as H2S, and CO2 in water to increase the pH. This speeds up the oxidation of iron and Manganese, improving processing efficiency.
The aeration phase will increase the amount of dissolved oxygen in the water, which has the effect of clarifying and removing color. There are two ways of aeration: bringing water into the air and bringing air into the water.
4. Chlorination
Pumping chlorine gas (Cl2) into the water has a strong antiseptic effect.
→ Note that chlorine gas turns Ammonia (NH4) present in water into Chloramine (monocloramine NH2Cl, dichloramine NHCl, triclonitr NCl) reduces the sterilization effect. Chloramines are also very toxic to the human body.
→ In addition, chlorine reacts with dissolved organic substances to form Trihalomethane are carcinogens to humans. Therefore, chlorination should not be used for surface water containing a lot of organic matter.

5. Coagulation and floc formation
Use agents capable of binding substances suspended in water into flocs. Can settle in settling tanks or filter media. The agent can be alum (PAC – Poly Aluminum Chloride) or polymer (polyacrylamide – PAM).
→ It is during this period that ARK Vietnam provides polymer mixing tank equipment , polymer to generate coagulants. Finally, our decanting centrifuge separates the colloidal particles from the water to form a sludge.
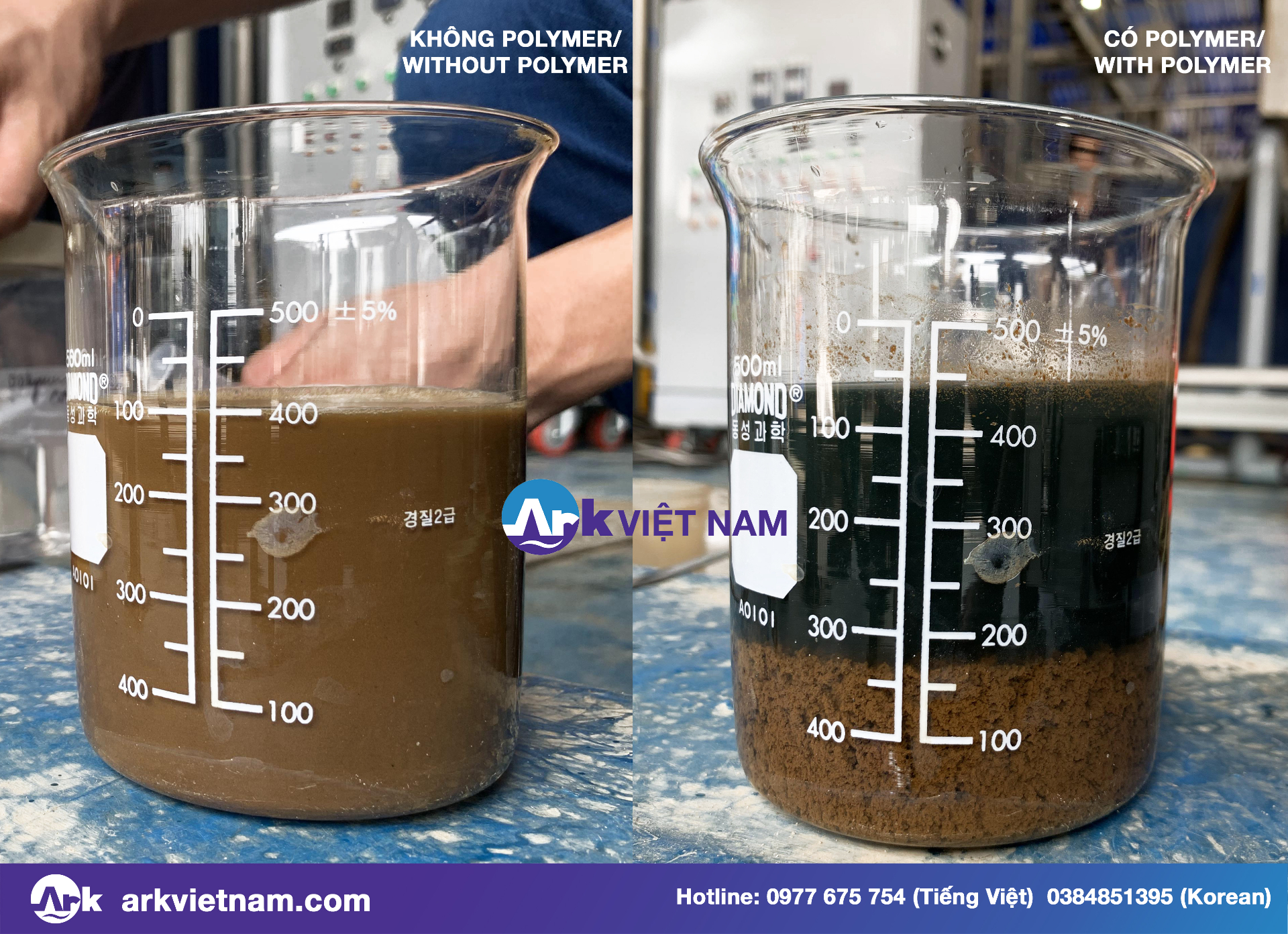

The agent chemicals must be prepared as a soluble solution. This solution is made by rapidly and evenly mixing alum (PAC) or polymer (PAM) with water. The solution concentration needs to be carefully calculated for maximum efficiency of the deposition process. In order to avoid chemical waste, resulting in higher overall disposal costs.
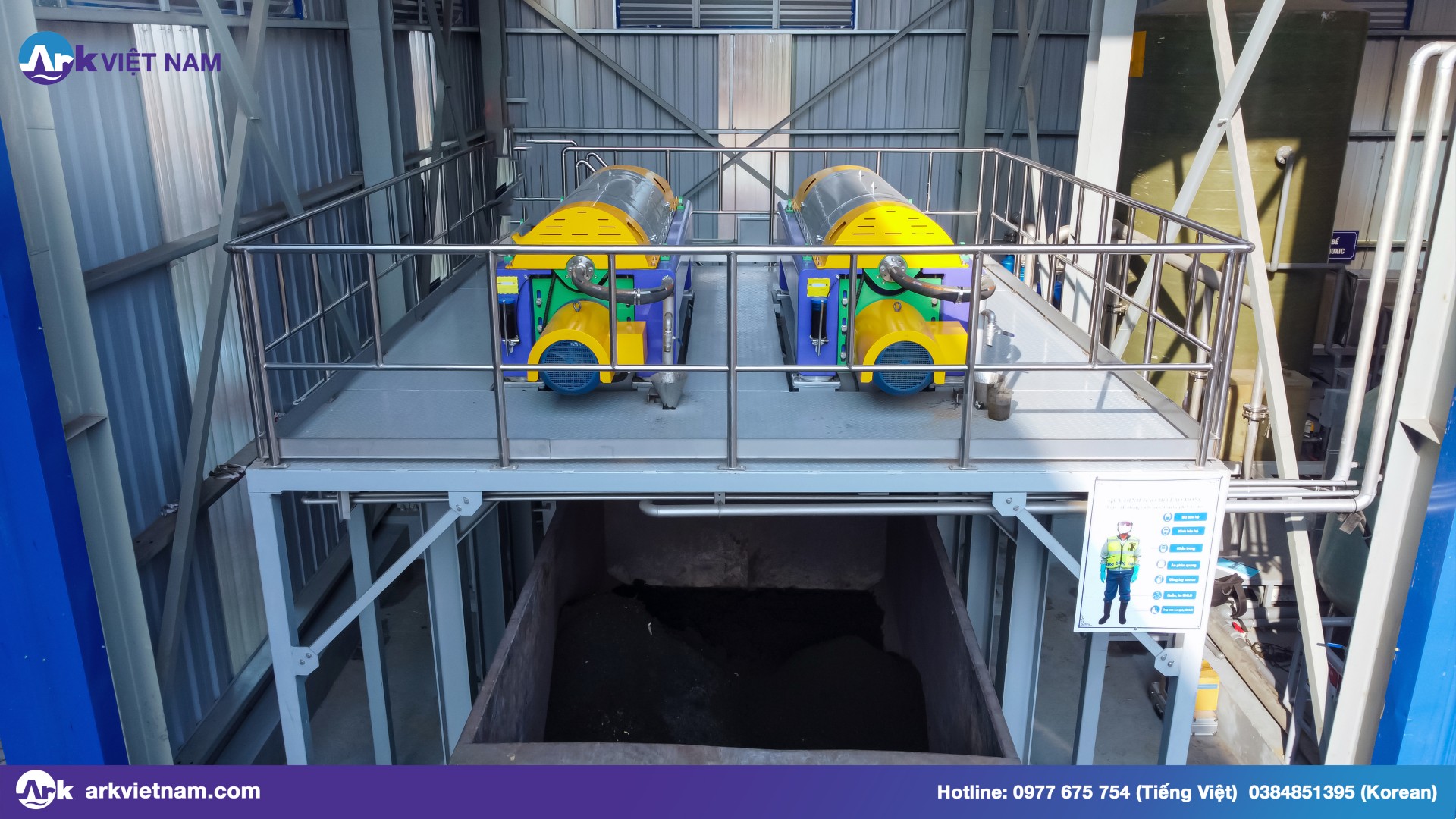

→ If the water plant does not use a sludge dewatering machine, sedimentation and filtration are the next processes after flocculation:
6. Sedimentation tank stage
Simply using gravity, the colloidal particles will settle to the bottom of the tank on their own. Or with the decanting centrifuge is to use centrifugal force rotation. Some flotation tanks use the repulsion of air bubbles. Most bacteria and their spores will also attach to the flocs.
7. Filters and absorbs odors
Filter to remove organic colloidal particles and colloidal iron. This makes the water cloudy. That creates mud. Activated carbon can absorb gaseous molecules and chemicals in liquid form. This stage has two common ways:
- Put the treated water into the filter directly at the activated carbon filter tank.
- Dilute activated carbon powder, which has been pulverized to microscopic size, with alum into the inlet source water tank.
Using a decanter centrifuge to treat feed water
Reading this far, you can imagine what stage the sludge dewatering machine will be used in a water treatment process.
Waste sludge is the floc formed from Physico-chemical processes, settling, and filtering. However, they still exist mainly in the dissolved form. The sludge solution is still composed mainly of water. The mass and volume are therefore extremely large (because of the inherently high density of water).
The sludge dewatering machine will help to filter most of the water from the sludge, dry it, and facilitate disposal. The water supply plant will reduce the cost of building and maintaining huge sludge tanks, or having to hire outside third-party units to remove and collect.
Different from belt press or filter press – the most popular types of mud presses on the market today. The decanter centrifuge uses advanced new technology, which comes with countless advantages worth the money.
See more: Structure and working principle of decanter centrifuge
Outstanding advantages of decanter centrifuge with other machines
- Decanter centrifuge water treatment can work continuously, automatically controlled, do not have to stop between pressing batches like plate frame machines. Helping to improve productivity, reduce operating costs, and save energy.
- Compact, self-contained design, no odor, saving installation space. Material made of stainless steel, eternal life.
- Easy to clean, save water.
- The decanter centrifuge processes juices of many sludges, including those containing chemicals and metals. The pressed sludge has high dryness and stability.
- Made in Vietnam, so it's easy to maintain, replacement parts are always available.
See more: Why are sludge presses necessary for the wastewater treatment system?
ARK VIETNAM –
Prestigious and quality water treatment centrifuge manufacturing and distribution unit
We use the most modern production line imported from Korea, accompanied by a reputable maintenance service.
Not every brand has a staff that is always ready to maintain the decanter centrifuge. As well as providing replacement parts quickly. Customers often have to wait many months just to wait for components from abroad.
The reason is that other manufacturers import sludge dewatering machines from Taiwan or China. ARK is the complete opposite. We have a factory and direct assembly in Vietnam.
Accompanied by a professional, dedicated after-sales service. Our hotline is always open 24/7 ready to serve customers. ARK regularly inspects installed products, fixes, and repairs in time. Bring maximum performance to your processing system.

When choosing ARK Vietnam, you will never be disappointed
Phone number: 0977.675.754 (Mr Truc)Website: www.arkvietnam.com
Email: arkvn234@gmail.com
Hanoi Office: 5th floor, N03-T7 Diplomatic Urban Area, Xuan Tao Ward, Bac Tu Liem District, Hanoi.
HCMC Office: 68 - 70 Hoang Dieu Street, Ward 13, District 4, HCM City.
