Wastewater from the food processing industry is diverse in composition and pollutant concentration, requiring suitable design technologies for production facilities. In this article, we will explore the sources of wastewater in the food processing industry and the sustainable treatment solutions proposed by ARK Vietnam.

Sources of wastewater in the food processing industry
- Initial food processing stages, such as sorting and cleaning raw materials.
- Processing of food products from raw materials.
- Cleaning and maintenance of processing machinery and production areas.
- Domestic wastewater from workers' sanitation and bathing facilities.
- Wastewater from cooking and dining areas within the factory.
Characteristics of food processing wastewater
Due to the diversity of food production and raw materials, the characteristics of wastewater also vary. Typical food processing wastewater contains:
- High levels of nitrogen and phosphorus.
- Relatively high concentrations of TSS (Total Suspended Solids), BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand), COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand), and bacteria.
- Some types of wastewater may contain salt, color, and starch.
- Substantial and stable flow.
- Organic matter (usually not highly toxic) from animal and plant sources.
Commonly used wastewater treatment technologies
| Parameter | Unit | First value | QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT Cột A | QCVN 40:2011/BTNMT Cột B |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | – | 6,5 – 8,5 | 6 – 9 | 5,5 – 9 |
| BOD5 | mg/l | 700 – 2000 | 30 | 50 |
| COD | mg/l | 1000 – 3500 | 75 | 150 |
| TSS | mg/l | 350 – 700 | 50 | 100 |
| Total Nito | mg/l | 100 – 350 | 20 | 40 |
| Total Phosphorus | mg/l | 30 – 100 | 4 | 6 |
| Grease | 50 – 200 | 5 | 10 | |
| Total Coliform | MPN/100ml | 104– 105 | 3,000 | 5,000 |
Công nghệ xử lý nước thải chế biến thực phẩm thường dùng
ARK Vietnam proposes suitable wastewater treatment solutions based on the diverse characteristics of the wastewater:
- Flotation-Filtration Technology: This process is effective in removing BOD, fats, oils, and suspended solids from wastewater containing high organic matter, such as those from vegetable and fruit processing.
- Flotation-Aeration-Anaerobic-Aeration: Suitable for treating wastewater from fast-food processing, seafood, fish-ball production, with high concentrations of oils, fats, or suspended matter.
- Grease Separation-Aeration-Anaerobic-Aeration MBBR (Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor) with pressure filtration: Applied to wastewater with high concentrations of oils, fats, and low suspended solids, like fish sauce processing.
- Chemical and mechanical treatment methods: These are used in industries with high pollution levels, such as slaughterhouses or fish sauce production, and can be combined with chemical treatment methods like flocculation and flotation.
Food processing wastewater treatment process
The treatment of food processing wastewater at the plant is carried out through several stages: Grease Interceptor, Aeration Tank, Physical-Chemical Flotation, and Biological Treatment. This way, the waste is efficiently treated, meeting water quality standards before being discharged into the environment.
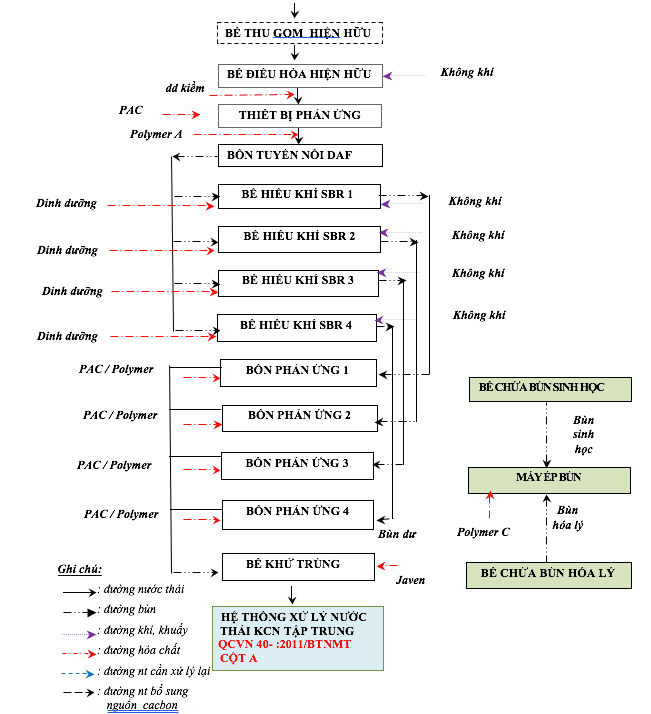
1. Preliminary Treatment
Collection tank stage
- Before entering the collection tank, the wastewater is removed with large garbage by coarse screens.
- The collection tank is the place to receive domestic and production wastewater from workshops in the factory.
- Wastewater is pumped through the conditioning tank by a submersible pump.
- The sewage pump works alternately in two modes: Automatic and Manual.
- The float is connected to the pool pump to signal when the tank is full or empty.
Conditioning tank stage
- The conditioning tank helps to regulate the flow and concentration of pollutants in the wastewater to avoid microbiological shock.
- Wastewater is then pumped into the high-speed spiral rig by two submersible pumps to start the physicochemical treatment cycle - flotation.
- Two sewage pumps operate alternately in two modes: Automatic and Manual.
- The float is connected to the conditioning tank pump to signal when the tank is full or empty.
2. Physicochemical treatment – flotation stage
- Wastewater is pH balanced through NaOH filling system to ensure high flocculation efficiency.
- The PAC coagulant is added to create floc from the “colloidal” particles.
- Polymer coagulant is also added to bind flocs together, forming larger flocs and improving pollutant removal efficiency.
- Wastewater from the high-speed spiral rig is led through the flotation tank to continue the treatment process.
The air is dissolved under pressure into the wastewater and pumped directly into the flotation tank. After entering the tank, air pressure is generated and combined with water, will saturate with air bubbles less than 100 microns in size. The tiny air bubbles create a specific gravity that adheres to the suspended solids in the water and lifts the suspended particles to the surface of the liquid, forming a floating slurry that is removed by the surface rake. This amount of board is taken to the physicochemical sludge tank.
3. Biological Treatment Stage
- The SBR batch aeration tank is the main biological treatment stage.
- SBR works in a cyclic cycle with 5 phases: Filling, Aeration, Settling, Draining, and Resting.
- In the aeration phase, the wastewater is aerated to create a biological reaction between the wastewater and the activated sludge or to supply oxygen to the water and stir the mixture.
- Nitrification from Nitrogen Ammonium takes place during this stage.
- The biological settling stage helps to settle the microbial flocs to the bottom, and at the same time collects water on the surface of the tank.
- The sludge generated during the treatment process is brought to the sludge tank and then pressed and treated according to regulations.
The nitrification process
The process of nitrification from ammonium nitrogen is divided into two steps and involves two types of microorganisms, namely Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacteria. In the first step, ammonium is converted to nitrite, and in the second step nitrite is converted to nitrate.
- Step 1. NH4– + 1,5 O2 –> NO2– + 2H+ + H2O
- Step 2. NO2– + 0,5 O2 –> NO3–
The Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacteria use the energy derived from the above reactions to sustain themselves and synthesize biomass. The process can be summed up by the following equation:
NH4– + 2 O2 → NO3– + 2H+ + H2O (*)
New biomass synthesis
- Oxidation and decomposition of organic matter:
Organic matter (BOD) + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy
- New cell synthesis:
Organic matter (BOD) + O2 + NH3 → Microbial cells + CO2 + H2O + energy
- Endogenous decomposition:
C5H7O2N + O2 → CO2 + H2O + NH3 + energy
The entire oxidation and synthesis reaction is shown by the following reaction
NH4+ + 1,83O2 + 1,98 HCO3– –> 0,021C5H7O2N + 0,98NO3– + 1,041H2O + 1,88H2CO3
The amount of oxygen required to oxidize ammonium to nitrate requires 4.3 mg O2/ 1mg NH4+. This value is close to the value of 4.57 commonly used in design calculation formulas.
4. Finishing Processing Stage
Disinfection tank
- The disinfection tank stores and disinfects water by eliminating pathogenic microorganisms. The chemical used for disinfection is chlorine compounds (Javen).
- Sodium Hypochlorite (NaOCl) is commonly used for disinfection due to its high bactericidal effectiveness and relatively low cost.
- The water disinfection process occurs in two stages: first, the disinfectant diffuses through the microbial cell walls, and then it reacts with enzymes inside the cell, disrupting metabolic processes, leading to microbial destruction.
- The effluent water meets Column B, QCVN 40-MT: 2011/BTNMT National Technical Regulation on Industrial Wastewater before being discharged into the centralized wastewater collection system of the industrial zone
Sludge Treatment
- Sludge generated during the physical-chemical and biological treatment is directed to the sludge container.
- Here, chemical polymer is added to the physical and biological sludge, and it is then sent to the Sludge Dewatering.
- The sludge after pressing is collected and treated by waste treatment units according to regulations
Conclusion
Treating wastewater from the food processing industry is a challenge. However, with the application of advanced technologies like physical-chemical flotation, SBR, and disinfection tanks, ARK Vietnam ensures that the wastewater treatment process is efficient, sustainable, and compliant with environmental standards.
